WHAT IS ALS?
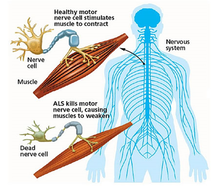
ALS is a progressive neurological disease that attacks the body’s nerve cells (or “motor neurons”) that are responsible for controlling voluntary muscle movement -- the muscles that we choose to move to produce movements like chewing, walking, and talking, and breathing.
When motor neurons degenerate and die, muscles no longer receive signals from the brain that they need to move. Unable to function, the muscles gradually weaken and atrophy (waste away). Eventually, the ability of the brain to start and control voluntary movement is lost.
ALS is a progressive neurological disease that attacks the body’s nerve cells (or “motor neurons”) that are responsible for controlling voluntary muscle movement -- the muscles that we choose to move to produce movements like chewing, walking, and talking, and breathing.
When motor neurons degenerate and die, muscles no longer receive signals from the brain that they need to move. Unable to function, the muscles gradually weaken and atrophy (waste away). Eventually, the ability of the brain to start and control voluntary movement is lost.
|
What are the early symptoms?
If you have any of these symptoms and/or you think you might have ALS, contact a neurologist and/or your general practitioner for their expert guidance. |
How does ALS affect the body?
As the disease progresses, muscle weakness and atrophy spread to other parts of your body:
|



